Abstract
Background: In RERISE phase 3 study, radotinib demonstrated significantly higher and faster rates of major molecular response (MMR) than imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP. By 36 months follow up, MMR (BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.1%) and MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.0032%) in radotinib 300 mg twice daily (bid) were higher than imatinib group. Also, early molecular response (EMR) at 3 months could predict better long term outcomes in both radotinib and imatinib groups. Here, authors updated 48 months long-term benefits and risks of 300mg bid and imatinib 400mg qd from RERISE phase 3 study (NCT01511289).
Methods: RERISE study was randomized trial of radotinib 300 mg bid (n=79), radotinib 400 mg bid (n=81), or imatinib 400 mg once daily (qd) (n=81) in patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP. We evaluated long-term MMR and MR4.5, overall survival (OS), and progression-free survival (PFS) including safety data by 48 months.
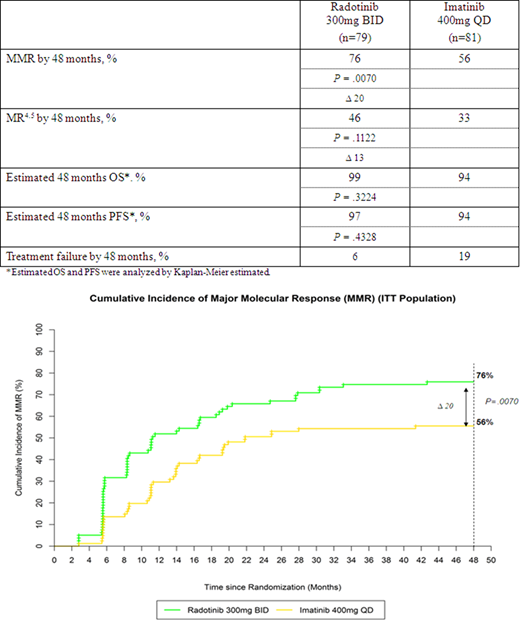
Results: At the study completion, 53% of patients with radotinib and 44% of patients with imatinib treated were remained. MMR and MR4.5 continued to be higher in patients receiving radotinib 300 mg bid compared with imatinib 400mg qd (Table). Especially, MMR rate by 48 months was significantly higher for radotinib compared to imatinib (76% vs 56%; P=0.0070, Figure). Also, early molecular response (EMR) at 3 months were observed in 86% of patients in the radotinib 300 mg bid group and 68% in the imatinib group (P = 0.0179). More patients treated with radotinib 300mg bid who had EMR at 3 months achieved MMR and MR4.5 by 48 months: 84% and 53% in the radotinib 300 mg bid group and 71% and 44% in the imatinib group, respectively. 48 months estimated OS and PFS rate were not significantly different in two groups (99% vs 94%; P=0.3224, 97% vs 94%; P=0.4328). Treatment failure was lower in radotinib group compared with imatinib group (Table).
The safety profiles were consistent with those previously reported and most of adverse events (AEs) developed within 12 months. No new or unexpected safety events were reported in both arms by 48 months and no serious CVE related with radotinib reported.
Conclusions: With a minimum 48 months follow-up, radotinib continued to demonstrate higher rates of MMR and MR4.5 than imatinib in newly diagnosed CML-CP. Also, these responses with radotinib were earlier and deeper compared with imatinib. Up to 48 months, no new and serious safety events related with radotinib reported. These results demonstrate that radotinib may have higher possibility of treatment- free remission (TFR) on frontline therapy as well as it can be one of the standards of care in newly diagnosed CML-CP.
Bunworasate:IL-YANG: Research Funding. Comia:IL-YANG: Research Funding. Mun:IL-YANG: Research Funding. Caguioa:IL-YANG: Research Funding. Kim:Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Ilyang: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal